JOINT SURGERY

Written by: Dr.Claire Arcidiacono, ND
For further questions or concerns email me at carcidiacono@invitehealth.com
No conversation involving joints and joint health could possibly be complete without talking about healing after having a joint repair surgery. To start with what types of surgeries are done to repair joints. How do I know if I need surgery? And just what should I take after surgery to help the healing process? Since this is a rather large topic, I will be breaking it into 2 parts. In this segment I will be discussing 3 of the 6 common procedures that your doctor may recommend. In this blog we will review the following: joint replacement surgery, arthroscopy, and osteotomy. In our next blog we will review the remaining 3 common procedures which involve resurfacing surgery, arthrodesis and small joint surgery. † (1)
One of the most well-known types of joint repair surgeries is joint replacement surgery. A joint replacement is performed when there is severe pain that does not respond to less invasive procedures. In addition to when there is extreme pain a joint replacement is recommended when a joint is damaged. For example, in osteoarthritis over a long period of time very often most if not all of the cartilage is worn away, this is known colloquially as bone on bone. This is an excellent example of a time when joint replacement is usually recommended by a doctor. Joint replacement is exactly what it sounds like. In this procedure the damaged portion of the joint is replaced with a prosthetic joint. (2) Please see the following picture for an example of a joint replacement. † (3)
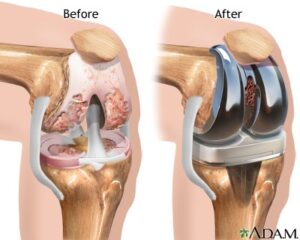
This is commonly performed on the shoulder joints, the knee joints and the ankle joint. Before a joint replacement is performed a complete work up is required. This can involve an ECG as well as certain blood tests. It is also important to review any supplements you may be taking at this time. Most likely your doctor will want you to stop anything that is even potentially a blood thinner. While everyone has a slightly different personal experience in regard to how long a joint replacement will last in general a joint replacement tends to last 10 years or more before it needs to be replaced. In general, a joint replacement surgery is considered a more invasive procedure. It would be remiss of me to not mention that it does have a risk of certain complications. These can include but are not limited to heart attack, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and pneumonia. Due to these possible complications, it is important to work with your doctor before the joint damage gets to this level. Once it gets to this level it is important to find a doctor you trust to discuss this option. † (4)
The next procedure we will be discussing is arthroscopy. This is considered to be a minimally invasive procedure. This procedure is normally done to treat injuries to the meniscus and AC ligaments. It can also be used to repair various conditions that occur in in the hip joint. In the shoulder it can help with osteoarthritis as well as rotator cuff tears, frozen shoulder, tendonitis, joint instability and even to remove foreign bodies from the joint. In the spine arthroscopic procedures can help treat disc problems, spinal deformity’s and even help in cases of trauma. Arthroscopic procedures have also been used in cases of spinal cancer. Arthroscopy is performed using an arthroscope that is inserted into the joint via a small incision. A camera is used to visualize inside the joint and project the imagine on a screen. In order to work inside the small incision, the doctor uses saline to distend the joint making room for the surgery to occur. Additionally, the doctor will use tools that are made especially small in order to fit into the space. This means that unlike in the joint replacement surgeries the joint doesn’t need to be completely opened up. This means that arthroscopy is less invasive than the previously discussed joint replacement surgery. As a result of being less invasive there is also much less risk of complications. Still just like with any procedure there is still risk of complications and you should discuss them with your doctor to see if this is the best option for you. † (5)
ICYMI: JOINT HEALTH SERIES: LAB WORK>>READ NOW!
The last procedure we will be discussing today is called osteotomy. This is considered an in between type of procedure. While it is more invasive than arthroscopy it is less invasive than a joint replacement surgery. This procedure can be helpful in cases of RA, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, gout and pseudo gout among other conditions. This procedure involves cutting and reshaping a bone near a damaged joint to minimize the stress on the affected joint. This is normally performed on younger people who are trying to delay a needed joint replacement for as long as possible. Most common complications form osteotomy can include blood clots as well as failure to heal properly. (6) Please see the attached picture for an example of what this procedure would look like in a joint. † (7)
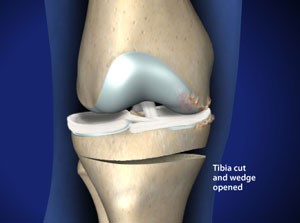
In our next blog we will finish talking about surgeries and talk about supplements that can help heal after a procedure. †
REFERENCES
- https://www.orthomedctr.com/joint-reconstruction.php
- Joint Replacement Surgery and You. (April, 2009) In Arthritis, Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease online. Retrieved from http://www.niams.nih.gov/#.
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002974.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joint_replacement#cite_note-NIAMS-1
- Jameson, S. S.; Dowen, D.; James, P.; Serrano-Pedraza, I.; Serrano-Pedraza, Deehan; Reed, M. R.; Deehan, D. J. (October 2011). “The burden of arthroscopy of the knee: a contemporary analysis of data from the English NHS”. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. 93 (10): 1327–1333. doi:1302/0301-620X.93B10.27078. ISSN 2044-5377. PMID 21969430.
- https://www.brighamandwomens.org/medical-resources/osteotomy-procedure
- https://www.joint-surgeon.com/knee/tibial-osteotomy-open-wedge


