More than 29 million people in the United States have diabetes and 1 out of 4 of them have no idea.[1] In honor of National Diabetes Month this November, InVite® Health is urging you to take some time to understand the risk factors and preventative measures of this disease.
Diabetes is a vicious and life-threatening disease, where your blood sugar is continuously and seriously elevated (and your triglycerides are also). The excess circulating blood sugar is very destructive inflaming tissues in the heart and circulation, in the eyes, brain, kidneys, and nerve tissue leading to all manner of serious and life-threatening diseases.
This condition occurs due to various reasons, as your cells become resistant to the effects of the hormone insulin (stores sugar in your cells). However, long before full-blown diabetes occurs, at a stage referred to as pre-diabetes, your blood sugar is already modestly increased and the beginnings of damage to your kidneys, your blood vessel walls, and to your eyes is already occurring (perhaps it should be renamed early-stage diabetes); even a modest elevation in blood sugar should always be looked at seriously.
There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational. Type 1 occurs because the body cannot make its own insulin to regulate blood sugar. It is less common in comparison to Type 2 and is not preventable. Type 1 refers to an autoimmune disease that attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas; it is much less common. People with Type 1 always require insulin. Type 2 occurs when the body does not use insulin well or cannot regulate the blood sugar levels with the insulin it has. Nine out of ten people with diabetes have Type 2 diabetes, a preventable, more common disease that occurs when the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin. This results in elevated levels of sugar and triglycerides in the blood. The most common cause of Type 2 diabetes is truncal obesity or having an apple-shaped body instead of a pear-shaped one. New evidence indicates that an increase in the circulating levels of CRP (C-reactive protein), an enzyme tied into inflammation and heart disease, is a major indicator of impending diabetes. Gestational diabetes (GA) occurs during pregnancy and occurs when the body is not able to produce or use the insulin needed during pregnancy.
According to the Center of Disease Control and Prevention, here are the major risk factors:
- Being overweight
- Being 45 years or older
- Having a parents or sibling with type 2 diabetes
- Being physically active less than 3 times a week
- Ever having GA or giving birth to a baby that weighs more than 9 pounds
- Race/ethnicity may affect your risk – African-Americans, Hispanics/Latino Americans, American Indians, Pacific Islanders and some Asian Americans are at a high risk of Type 2.
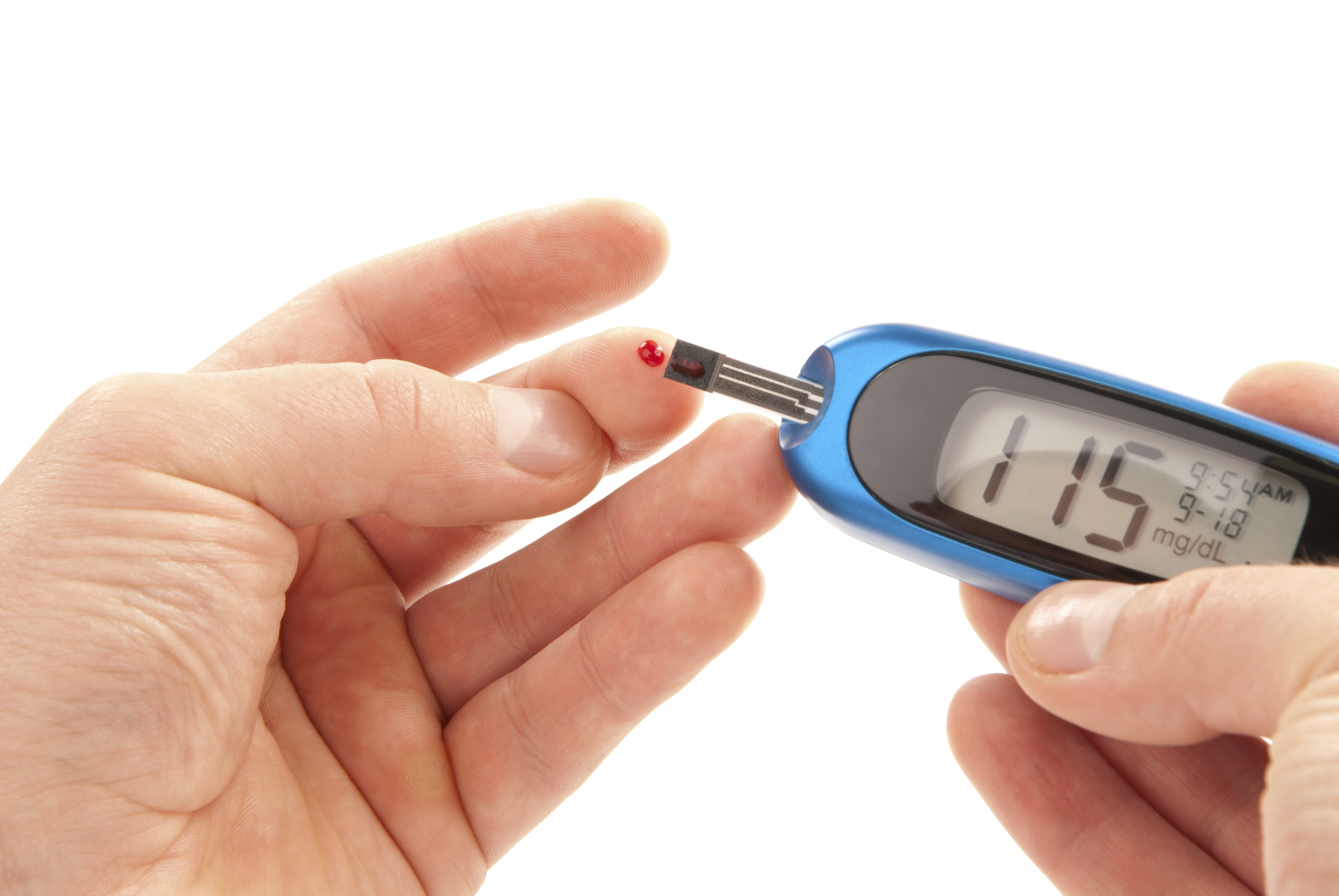
To determine your risk of developing this condition, your doctor will perform a blood test after you fast for 12 hours. If your blood sugar after fasting is lower than 99, you are likely normal. However, if the blood sugar is between 100 to 125 mg/dL you have impaired fasting blood glucose and your risk of developing diabetes is increased. You are also at risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
For many individuals diet, exercise, and particular nutrients are very beneficial at this point and can help restore blood sugar levels down towards normal. Some drugs are also prescribed for this effect. If your fasting blood sugar is above 125mg/dL you are considered to have full-blown diabetes and it must be treated aggressively.
Being diagnosed with this condition means you will have to constantly be sure your body is balanced – your food consumption, activity level, medication and blood sugar levels. Here are some tips from the CDC on how to manage your diabetes on a daily basis:
- Follow a healthy diet
- Be sure to be active for 10-20 minutes a day
- Regularly take your diabetes medicine prescribed by your doctor
- Test your blood sugar to understand and track your blood sugar levels
Managing this condition may be tedious, but keeping a record of your treatment plans, feelings and medications could help keep it manageable. Follow your ABCs– the A1C test, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol and (not) Smoking.
For more information on diabetes and how you can prevent it, visit http://www.cdc.gov/features/livingwithdiabetes/index.html.