Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Dr. Claire Arcidiacono, ND
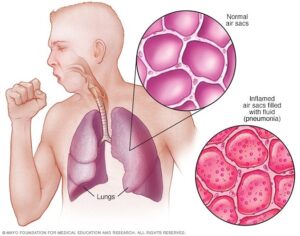
I wanted to finish up this series on respiratory health with a discussion on pneumonia. While pneumonia can be mild it can also become life threatening. What is pneumonia? Basically pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in the air sacs in one or both lungs. As a result of the inflammation the sacs may fill with fluid or pus which can trigger a cough. Please see the attached picture. (1)
What can cause pneumonia? Pathogens that usually cause pneumonia include bacteria, bacteria like organisms, fungi and viruses. Pneumonia is classified according to type of organism that causes it as well as where you acquired the infection. The first type is the most common and is called community -acquired pneumonia. As the name implies this occurs outside of hospitals or other health care facilities, or in other words “in the community”. The next type is called hospital acquired pneumonia. This tends to be caused by bacteria more than the other pathogens. Related to hospital acquired is health-care acquired pneumonia which is pneumonia that occurs in people who live in long-term care facilities or receive care in outpatient clinics such as kidney dialysis centers. Lastly there is aspiration pneumonia which is where you inhale food, drink, vomit or saliva into your lungs. This is more likely if there is a problem with your gag reflux.
While anyone can get pneumonia there are certain risk factors that increase your risk. To start with the 2 age groups most at risk are children under 2 and adults over 65. Being hospitalized and being on a breathing machine increase your risk. Having a chronic disease such as asthma or COPD increase your risk. Having a weak or suppressed immune system can also increase risk. Lastly smoking can also increase the risk of pneumonia.
What are the most common symptoms of pneumonia? Well you may have a cough with phlegm. There may be chest pain when you cough or breath. There may be fatigue as well as fever, sweating and shaking chills. Your digestive system may be affected resulting in nausea, vomiting or even diarrhea. In those over 65 there may be a lower than normal body temperature as well as confusion. (1)
When it comes to pneumonia it is important to talk about complications. Pneumonia can lead to bacteremia which is where bacteria literally get into our blood. Sounds series right? Well it absolutely is. Bacteremia can lead to septic shock. Pneumonia can also lead to lung abscesses which are pockets of puss in our lungs. Pneumonia can also cause what is called pleurisy, pleural effusions and empyema. If the pneumonia is severe it can lead to respiratory failure. Pneumonia can even lead to failure of certain organs such as the kidneys and heart. (2) As you can see pneumonia can haves dangerous complications. What can you do to help reduce the risk of pneumonia?
- There are a number of life style factors that can help. Talk to your doctor about whether or not a vaccine is right for you. Practice good hygiene. Have a food diet. Quit smoking. (3)
- Olive Leaf has been one supplement that has come up over and over again. In fact studies have found that Olive Leaf is helpful in ameliorating lung disease such as pneumonia. (4) Please see Invite’s Olive Leaf and Renalaid.
- Garlic, according to studies “could be used as an effective antibacterial nutrient” for pneumonia causing bacteria. (5) Please see Invite’s Aged Garlic.
- NAC is another nutrient that has come up frequently in this series. Studies have found that NAC may decrease the oxidative and inflammatory damage in pneumonia. (6) Please see Invite’s NAC.
- Black Seed has been found in studies to help slow the growth of bacteria such as those that are associated with pneumonia. (7) Please see Invite’s Black Seed formula.
Our last blog on this topic will be a nice summary to wrap things up before we move on!
Sources:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pneumonia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354204
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/complications-pneumonia
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pneumonia/prevention
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10295110/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12602248/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6250560/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348808654_EFFECTIVENESS_TEST_OF_BLACK_CUMIN_SEEDS_NIGELLA_SATIVA_EXTRACT_ON_THE_GROWTH_OF_KLEBSIELLA_PNEUMONIAE_AND_PSEUDOMONAS_AERUGINOSA_BACTERIA
