Written by Dr.Claire Arcidiacono, ND
For further questions or concerns email me at [email protected]

Last week we finished our conversation about lupus. Today we will be discussing gout. Gout will be the last condition specific blog in this series on joints. What exactly is gout? Basically, gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis in the joints. This arthritis is interesting because it is associated with uric acid build up in the joints. This uric acid causes the joints to become inflamed and this inflammation is what leads to the joint damage and pain. (1) Please see picture for exactly what this looks like. † (2)
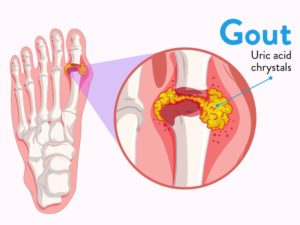
Symptoms of gout may sound familiar, interestingly gout usually starts in the joint of the big toe. As the condition progresses more and more joints become involved. Like other inflammatory disorders in gout the joints will be red, tender, swollen and even warm to the touch. In addition to joint pain the buildup of uric acid can also cause the buildup of crystals in the kidneys leading to what is known as urate nephropathy. In addition to these symptoms’ gout can also lead to systemic symptoms such as fatigue and even a high fever. † (3)
The symptoms of gout are caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals. Therefore, anything that increases the uric acid levels in the body will increase the risk of developing gout. Diet is a very well-known risk factor for gout. A diet high in alcohol, meat, seafood and sugar can increase the uric acid in the body and thus can increase gout risk. (4) Another well-known diet-based risk factor for gout is a diet that is high in purines which can increase uric acid. Purines are a part of every cell and break down into uric acid. Because they are found everywhere it is impossible to eliminate them entirely. It is possible to try and limit the foods that have a very high purine content. (5) These foods include but are not limited to anchovies, shrimp, mushrooms, seaweed and organ meats. (6) Some research has indicated that potatoes as well as chicken can increase the risk of developing gout. (7) As a result of the fact that gout occurs when uric acid builds up anyone that has kidneys that do not excrete the uric acid properly is at a higher risk of developing gout. † (8)
Certain genes have been found to increase the risk of developing gout. Therefore, anyone with a family history of gout may want to reduce their other risk factors for the disease. † (9)
Gout is associated with certain medications as well as certain chronic conditions. For example, diuretics, niacin, aspirin, ACE inhibitors as well as Beta blockers and even some chemotherapy may increase the risk of gout. (10) Interestingly with excessive vitamin D (blood work showing vitamin D over 80) there is an increased risk of gout. (11) A few examples of chronic conditions that are associated with gout include but are not limited to the following: metabolic syndrome, kidney failure, organ transplant recipients, those exposed to lead and those who are obese/overweight. † (12)
Other triggers that can lead to a gout flare up can include rapid changes in the weather. Additionally, trauma, surgery and having sleep apnea increase the risk of gout. † (13)
While having high uric acid on blood work or hyperuricemia is considered to be a classic sign of gout not everyone with gout has this classic sign. In fact, up to 50% of people with gout never develop high uric acid on blood work. (14) In order to diagnose gout uric acid crystals are found in the synovial fluid of the joints. (15) Other conditions that should be ruled out can include but are not limited to pseudo-gout, RA, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatism. † (16)
ICYMI:PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS>>READ NOW!
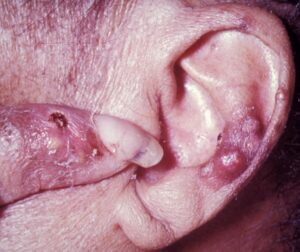
The goals of working with gout include stopping the acute attack or flare up that is occurring right now and then from there we work on lowering the uric acid. By lowering the uric acid, we can reduce the risk of a flare up in the future. Now I know some people might think that they only need to work on gout during a flare up but it’s important to work to reduce the uric acid levels regardless of flare up status. Each gout “attack” or flare up increases the risk of damaging the joint. This can lead to destruction of the joint surface and even cause the joint to become deformed. Lastly in 30% of those with untreated gout something called tophi can occur. This is basically a buildup of uric acid that most commonly occurs on the ear, olecranon process and the Achilles. † (17) Please see the attached picture (18) †
To help reduce uric acid and thus reduce the risk of gout the following have been found to be helpful:
- Low purine diets have been found to help reduce the uric acid and reduce the risk of a gout flare up.† (18)
- Potassium deficiency has been found to be associated with gout. Thus, taking potassium and correcting that deficiency can help the gout. † (19) Please see Invite’s Uric Hx
- Celery root has been found to reduce the risk of gout flare ups. † (20) Please see Invite’s Uric Hx
- Chanca Piedra root has been found in studies to reduce uric acid levels. † (21) Please see Invite’s Uric Hx
- Tart cherry has been found to lower uric acid levels and reduce the inflammation found in gout. † (22) Please see Invite’s Beets Hx
- Magnesium has been found to lower uric acid build up and help reduce gout flare ups. † (23) Please see Invite’s extensive line of magnesium products.
- Turmeric has been found to help with swelling and pain. † (24). Please see Invite’s Biocurcumin, and Curcumin blend.†
Next week we will be discussing how to heal from surgical based interventions. †
REFERENCES
- Abhishek, A; Roddy, E; Doherty, M (February 2017). “Gout – a guide for the general and acute physicians”. Clinical Medicine. 17 (1): 54–59. doi:7861/clinmedicine.17-1-54. PMC 6297580. PMID 28148582.
- https://www.bouldermedicalcenter.com/about-gout-causes-symptoms-and-treatment/
- Dalbeth, N; Merriman, TR; Stamp, LK (April 2016). “Gout”. Lancet (Review). 388 (10055): 2039–2052. doi:1016/S0140-6736(16)00346-9. PMID 27112094. S2CID 208790780.
- Neogi, T (July 2016). “Gout”. Annals of Internal Medicine (Review). 165 (1): ITC1-16. doi:7326/AITC201607050. PMID 27380294.
- https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/gout/what-are-purines
- Kaneko, Kiyoko; Aoyagi, Yasuo; Fukuuchi, Tomoko; Inazawa, Katsunori; Yamaoka, Noriko (2014). “Total Purine and Purine Base Content of Common Foodstuffs for Facilitating Nutritional Therapy for Gout and Hyperuricemia”. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 37 (5): 709–721. doi:1248/bpb.b13-00967. PMID 24553148.
- Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Willett W, Curhan G (March 2004). “Purine-rich foods, dairy and protein intake, and the risk of gout in men”. Engl. J. Med. 350(11): 1093–1103. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035700. PMID 15014182.
- Richette P, Bardin T (January 2010). “Gout”. Lancet. 375 (9711): 318–328. doi:1016/S0140-6736(09)60883-7. PMID 19692116. S2CID 208793280.
- Merriman, TR; Dalbeth, N (2011). “The genetic basis of hyperuricaemia and gout”. Joint Bone Spine. 78(1): 35–40. doi: 1016/j.jbspin.2010.02.027. PMID 20472486.
- Firestein, MD, Gary S.; Budd, MD, Ralph C.; Harris Jr., MD, Edward D.; McInnes PhD, FRCP, Iain B.; Ruddy, MD, Shaun; Sergent, MD, John S., eds. (2008). “Chapter 87: Gout and Hyperuricemia”. Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology (8th ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-1416048428.
- Chen, Yingchao (2020). “Association between serum vitamin D and uric acid in the eastern Chinese population: a population-based cross-sectional study”. BMC Endocr Disord. 20 (79): 79. doi:1186/s12902-020-00560-1. PMC 7268462. PMID 32493273. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- Weaver, AL (July 2008). “Epidemiology of gout”. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 75 Suppl 5: S9–S12. doi: 3949/ccjm.75.Suppl_5.S9. PMID 18819329. S2CID 40262260.
- Singh, JA; Reddy, SG; Kundukulam, J (March 2011). “Risk factors for gout and prevention: a systematic review of the literature”. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 23 (2): 192–202. doi:1097/BOR.0b013e3283438e13. PMC 4104583. PMID 21285714.
- Schlesinger N (March 2010). “Diagnosing and treating gout: a review to aid primary care physicians”. Postgrad Med. 122 (2): 157–161. doi:3810/pgm.2010.03.2133. PMID 20203467. S2CID 35321485.
- Rothschild, Bruce M. “Gout and Pseudogout Workup”. Medscape. Updated: Jun 30, 2020
- Schlesinger N (March 2010). “Diagnosing and treating gout: a review to aid primary care physicians”. Postgrad Med. 122 (2): 157–161. doi:3810/pgm.2010.03.2133. PMID 20203467. S2CID 35321485.
- Sriranganathan MK, Vinik O, Pardo Pardo J, Bombardier C, Edwards CJ (11 August 2021). “Interventions for tophi in gout”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2021 (8): CD010069. doi: 1002/14651858.CD010069.pub3. PMC 8406833. PMID 34379791.
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/52/Case_30-top.jpg
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6950134/
- https://ukrocharity.org/2014/08/top-news-on-uric-acid-and-gout/#:~:text=Gout%20can%20be%20triggered%20by,%25%20of%20cases%20%5BColton%5D.
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gout/can-different-parts-of-the-celery-plant-naturally-treat-gout#:~:text=The%20researchers%20found%20that%20luteolin,acid%2Dinduced%20inflammation%20in%20gout.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7073821/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5872714/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7750830/#:~:text=Practical%20Applications&text=This%20study%20found%20that%20acupuncture,joints%20afflicted%20with%20psoriatic%20arthritis.